Apple timber, like many perennial vegetation, endure a protracted juvenile stage earlier than reaching maturity, throughout which they expertise advanced developmental modifications. These transitions influence photosynthetic traits, progress charges, and hormone steadiness. Nevertheless, the mechanisms governing these processes will not be effectively understood, complicating efforts to boost fruit tree productiveness.
Given the financial significance of apple cultivation, researchers try to unravel these developmental cues. Addressing these complexities necessitates exploring genetic and physiological interactions that dictate progress methods, paving the best way for advances in agricultural practices and improved crop efficiency.
A examine from the State Key Laboratory for Crop Stress Resistance at Northwest A&F College, revealed in Horticulture Analysis, investigates sorbitol’s influence on progress transitions in apple vegetation. The findings present that sorbitol accumulation drives the shift from quick to sluggish progress as apple vegetation age. These insights spotlight essential genetic mechanisms regulating developmental transitions, setting the stage for future agricultural developments.
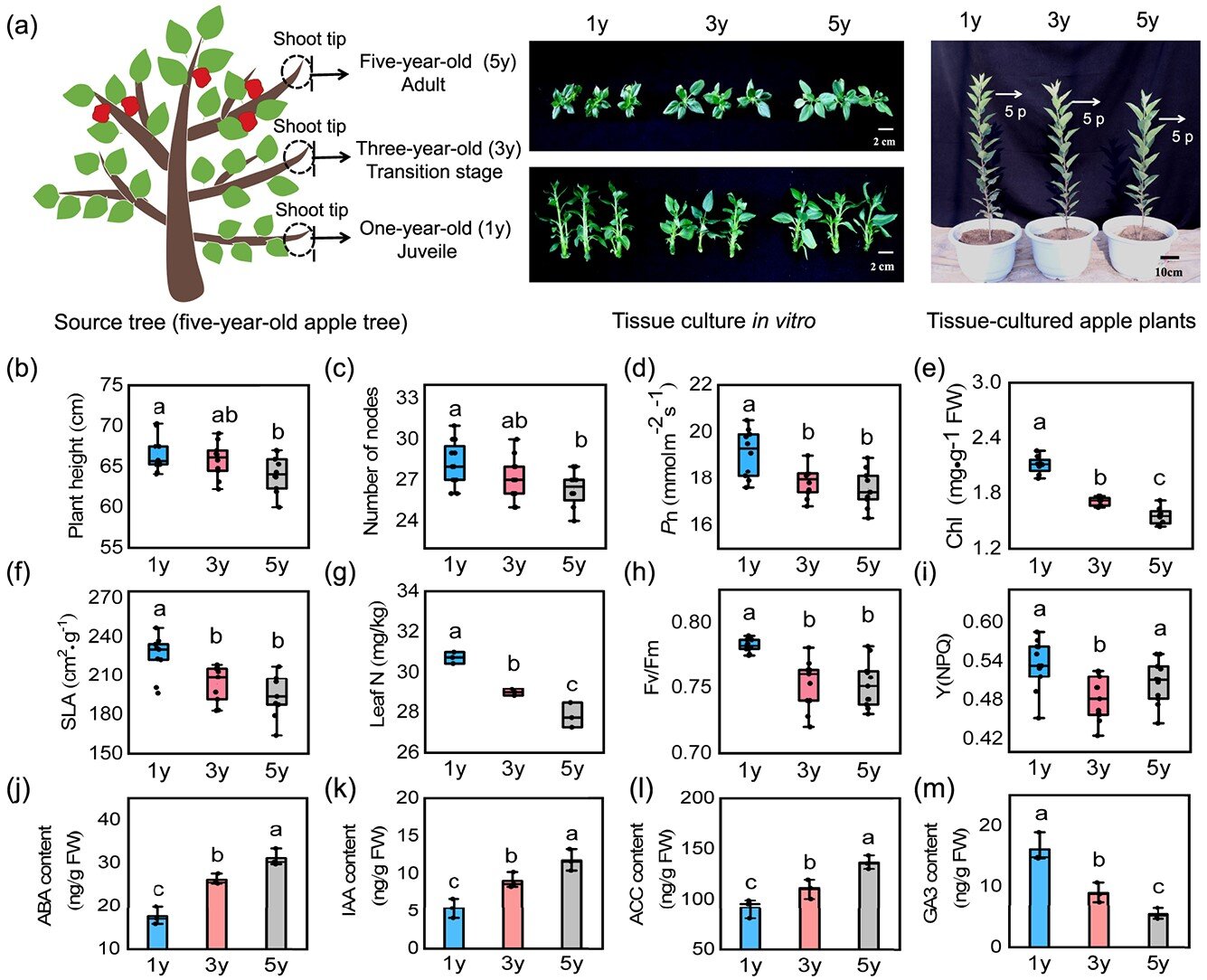
The examine particulars how apple vegetation endure vital age-dependent modifications, together with shifts in photosynthetic effectivity, hormone regulation, and carbon metabolism. Researchers utilized tissue-cultured apple vegetation to symbolize juvenile, transition, and grownup phases, measuring variations in plant top, photosynthetic charges, and hormone ranges.
A key discovering was the identification of MdSDH1, a gene essential for sorbitol breakdown, extremely energetic throughout the juvenile section. Suppressing MdSDH1 led to decreased gibberellin (GA3) ranges and plant progress, however exogenous GA3 restored these traits, underscoring the gene’s position in progress regulation.
The examine additionally revealed that amassed sorbitol prompts the MdSPL1-MdWRKY24 module, which suppresses growth-related genes and enforces a slow-growth technique. By linking metabolic and genetic alerts, the analysis emphasizes sorbitol’s twin perform as a carbon supply and a signaling molecule, enriching our understanding of apple tree growth.
Dr. Fengwang Ma, the senior writer, emphasised the examine’s significance, saying, “Our analysis uncovers how sorbitol and genetic regulators work collectively to manipulate apple plant progress. By understanding these intricate mechanisms, we will higher handle progress phases and increase agricultural productiveness. This examine not solely deepens our understanding of perennial plant growth but in addition units the inspiration for superior breeding and administration methods to optimize fruit tree efficiency.”
The findings symbolize a notable development in plant science, with the potential to revolutionize apple cultivation practices.
The analysis has far-reaching implications for the apple business, providing strategies to fine-tune tree progress and fruit yield by managing hormonal and metabolic pathways. By adjusting sorbitol ranges and the related genetic elements, breeders can develop apple varieties with enhanced progress traits and higher environmental resilience. Moreover, the examine sheds mild on regulating carbon and hormone dynamics to manage maturation pace, catering to numerous agricultural wants.
This work gives a strategic basis for enhancing fruit manufacturing and sustainability, addressing challenges posed by local weather change and useful resource constraints.
Extra data:
Xumei Jia et al, Sorbitol mediates age-dependent modifications in apple plant progress technique by way of gibberellin signaling, Horticulture Analysis (2024). DOI: 10.1093/hr/uhae192
Offered by
Horticulture Analysis
Quotation:
Candy change: Sorbitol’s key position in apple plant progress technique (2024, November 12)
retrieved 13 November 2024
from 2mD
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.