Pharmaceutical scientists from the National University of Singapore (NUS) have identified and characterized a unique multidomain enzyme capable of catalyzing two distinct types of reactions, both vital for making drug molecules.
Natural products produced by living organisms such as plants, animals, and microorganisms, govern various survival and defense purposes. However, these compounds can be repurposed as drugs and medicines. Many well-known drugs, including ibuprofen and penicillin, are derived from these natural products.
The biosynthetic enzymes responsible for the production of natural products create unique molecules that are often difficult for humans to replicate. Discovering new biosynthetic enzymes opens up the possibility of developing innovative drug molecules that could offer new therapeutics to treat life-threatening infections and cancer.
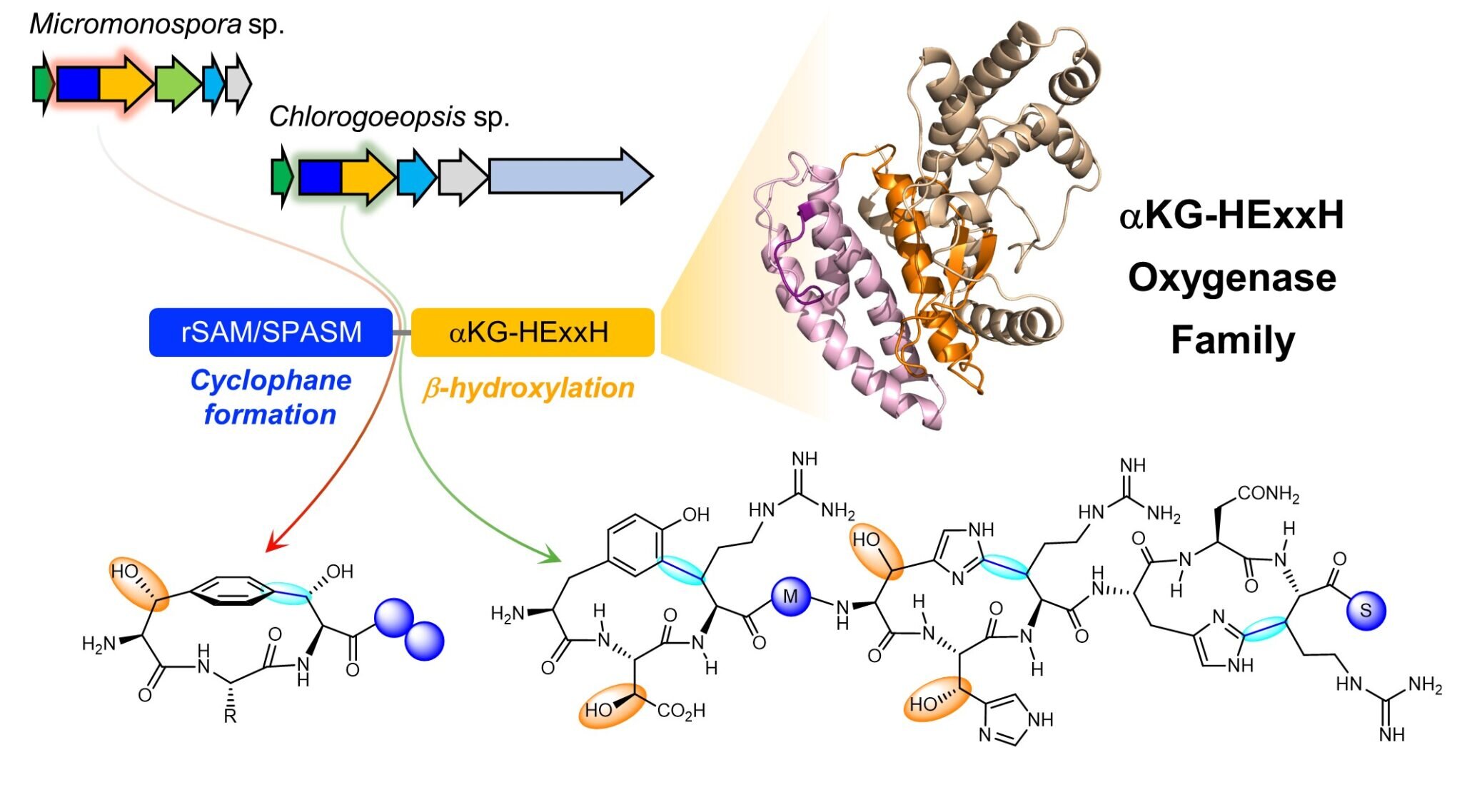
Led by Assistant Professor Brandon I. Morinaka from the Department of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences at NUS, researchers have identified multidomain enzymes that catalyze two reactions-cyclization and hydroxylation-on a single peptide substrate.
These bacterial biosynthetic enzymes may potentially provide new ways to create drug molecules, as both of these transformations are challenging to achieve through chemical synthesis.
In these systems, the enzyme contains two distinct domains: a radical SAM domain responsible for catalyzing cyclization and a hydroxylase domain for catalyzing hydroxylation. Interestingly, while the hydroxylase domain was initially predicted to be a protease based on its structural similarity to metalloproteases, the researchers discovered that it belongs to a new type of oxygenase family, termed αKG-HExxH.
This research was conducted in collaboration with Professor Qi Zhang at Fudan University, China and Professor Yvain Nicolet at the University of Grenoble Alps, France.
The findings were published in the journal Nature Chemistry.
Prof Morinaka said, “The combination of a multidomain protein for peptide modification and the discovery of a new oxygenase family will allow new avenues in natural products discovery and enzymology.”
These enzymes are remarkable because they represent a new protein design, capable of modifying peptides with two distinct domains simultaneously within a single protein. While previous enzymes have been shown to catalyze interrelated transformations, the reactions in this study are completely separate reactions.
These findings represent a new strategy for creating peptide drugs that could serve as next-generation treatments for infections and cancer.
“We are always amazed by the chemistry that nature has evolved. These reactions are difficult, if not impossible, for humans to design or imagine,” added Prof Morinaka.
Moving forward, the researchers aim to explore the potential therapeutic applications of the enzyme products, investigate how the enzymes catalyze such complex sequences of reactions, and engineer the systems to obtain an even broader range of new products.
More information:
Yohei Morishita et al, Fused radical SAM and αKG-HExxH domain proteins contain a distinct structural fold and catalyse cyclophane formation and β-hydroxylation, Nature Chemistry (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41557-024-01596-9
Provided by
National University of Singapore
Citation:
Unique multidomain enzymes from bacteria identified (2024, October 28)
retrieved 28 October 2024
from grb
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.