Researchers at Oxford College have developed a brand new methodology to extract fluorine from fluorspar (CaF2) utilizing oxalic acid and a fluorophilic Lewis acid in water below delicate response situations.
This expertise permits direct entry to fluorochemicals, together with generally used fluorinating brokers, from each fluorspar and lower-grade metspar, eliminating reliance on the availability chain of hazardous hydrogen fluoride (HF). The findings had been printed within the journal Nature.
Presently, all fluorochemicals—vital for a lot of industries—are generated from the extremely harmful mineral acid hydrogen fluoride (HF). This acid is produced in a high-energy course of whereby naturally occurring fluorspar (CaF2) is reacted with concentrated sulfuric acid below very harsh situations. Regardless of stringent security laws, HF spills have occurred, generally inflicting fatalities and detrimental environmental results.
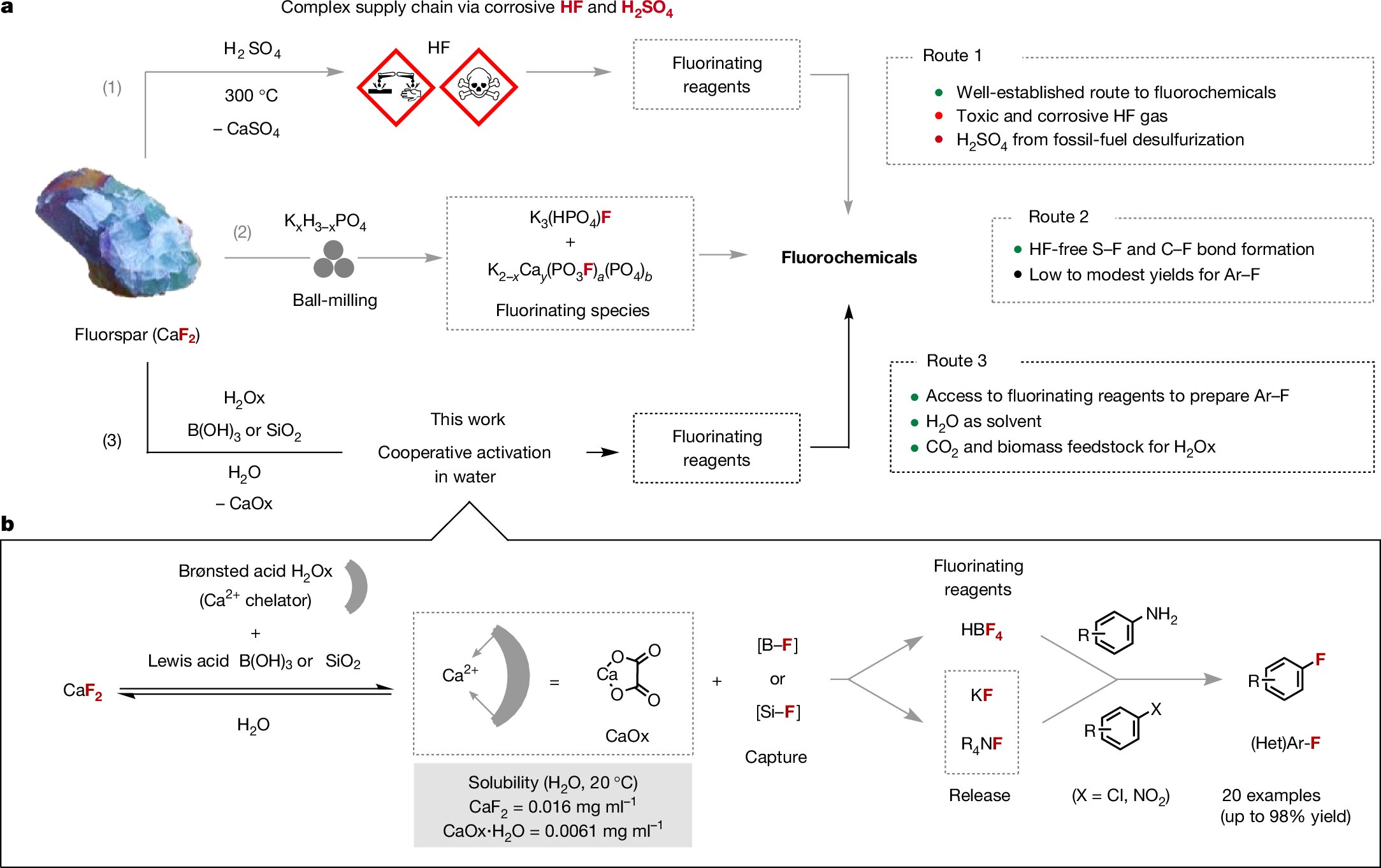
A crew in Oxford has now demonstrated that the fluorine content material of acid grade fluorspar (>97% CaF2) will be harvested in water below delicate response situations within the presence of a fluorophilic Lewis acid and oxalic acid serving as Brønsted acid. This follows earlier work by the crew into solid-state activation of fluoride utilizing mechanical power.
Their new aqueous response pathway is adaptable, relying on the Lewis acid used. With boric acid, the method affords an aqueous resolution of tetrafluoroboric acid that was efficiently utilized to Balz-Schiemann chemistry.
When silica is used as a substitute of boric acid, this scalable course of carried out at room temperature gives direct entry to aqueous hexafluorosilicic acid that may be transformed into generally used nucleophilic fluorinating reagents reminiscent of potassium fluoride and tetraalkylammonium fluoride salts.
This work represents a brand new departure for the manufacturing of fluorochemicals from fluorspar, in addition to lower-purity metspar, as a result of the protocol doesn’t depend on the complicated provide chain of hazardous HF. Contemplating present efforts to organize oxalic acid at a low price from CO2 and biomass, the tactic could change into a viable different to the standard sulfuric acid-dependent HF pathway.
Dr. Simon Immo Klose, previously on the College of Oxford and now at Columbia College (U.S.), and one of many lead authors of the research, says, “Essentially the most difficult side of utilizing fluorspar as a fluoride supply is its excessive stability and low solubility.
“Not like desk salt, which dissolves readily in water, solely a tiny pinch of fluorspar would dissolve in the identical quantity of water. However, like pulling a thread to unravel a whole sweater, if we are able to regularly take away this tiny quantity, we are able to dissolve kilograms of calcium fluoride below delicate situations, regardless of its low solubility.”
Dr. Anirban Mondal, from the Division of Chemistry, College of Oxford, and one of many lead authors of the research, says, “HF-related accidents function a continuing reminder of the hazards concerned in conventional fluorochemical manufacturing. With our expertise, nevertheless, we are able to immediately entry all of the generally used fluorinating reagents from fluorspar with out having to depend on HF and its hazardous provide chain.
“It’s extremely rewarding to be a part of a crew engaged on such a sensible, real-world downside with an answer that can instantly have an effect.”
Calum Patel, previously on the College of Oxford and now at FluoRok (UK), and one of many lead authors of the research, says, “Our first mechanochemical methodology disclosed in 2023 [Science] led to a brand new reagent that was studied for its capability to function nucleophilic fluoride.
“We’ve got taken a considerably completely different, but complementary strategy to processing fluorspar into well-known industrially necessary fluorinating reagents. Remarkably, fluorspar will be activated in water at low temperature by way of the cooperative motion of oxalic acid and a Lewis acid.
“This course of permits us to entry broader lessons of fluorochemicals from fluorspar with out the necessity to manufacture HF, reminiscent of structurally numerous fluoroarenes used to synthesize agrochemicals.”
Lead writer Prof Véronique Gouverneur FRS, Division of Chemistry, College of Oxford, who conceived and led this research says, “An answer to make use of CaF2 immediately for fluorination chemistry, with out the necessity for HF manufacturing, has been sought for many years. This research represents an necessary step as a result of the protocol developed in Oxford is simple to implement and doesn’t require specialised gear.
“It will possibly subsequently be used wherever in academia and trade, minimizing carbon emissions by avoiding HF manufacture and enabling provide localization.”
Extra data:
Immo Klose et al, Fluorspar to fluorochemicals upon low-temperature activation in water, Nature (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-08125-1. www.nature.com/articles/s41586-024-08125-1
Offered by
College of Oxford
Quotation:
Fluorspar activated in water below delicate situations gives new path to fluorochemicals (2024, November 13)
retrieved 13 November 2024
from CQ5
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.