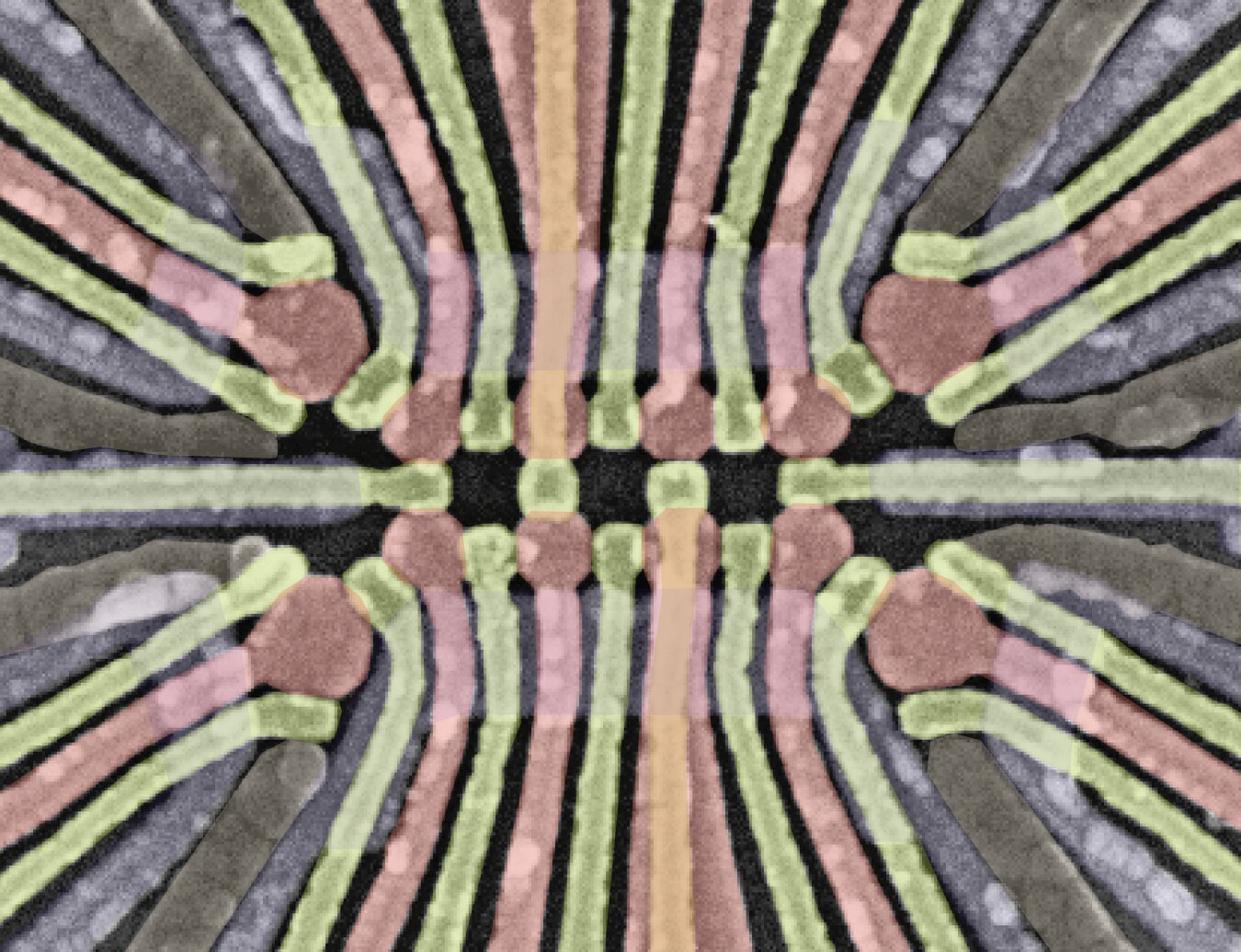
Having the ability to exactly manipulate interacting spins in quantum methods is of key significance for the event of dependable and extremely performing quantum computer systems. This has confirmed to be notably difficult for nanoscale methods with many spins which might be based mostly on quantum dots (i.e., tiny semiconductor units).
Researchers at Delft College of Expertise (TU Delft) not too long ago demonstrated the common management of a quantum dot-based system with 4 singlet-triplet qubits. Their paper, revealed in Nature Nanotechnology, might open new potentialities for the profitable upscaling of quantum data processing methods.
“We had been initially making an attempt to tune up and calibrate the change interplay between all of the neighboring spins in a 4×2 quantum dot array, loaded with one spin per dot,” Lieven Vandersypen, senior creator of the paper, informed Phys.org.
“We used time area measurements to do that, and sooner or later, we realized that we successfully achieved common management of 4 so-called singlet-triplet qubits (joint states of two spins). We subsequent made an excellent effort to rigorously benchmark the quantum operations and to create entanglement throughout the qubit array.”
Earlier than this research, quantum physicists and engineers had been capable of attain common management of methods with as much as two interacting singlet-triplet qubits. Vandersypen and his colleagues had been thus the primary to attain management over a bigger quantum dot-based system with 4 singlet-triplet qubits.
“Every qubit in our system consists of two spins and single-qubit operations will be managed by baseband voltage pulses,” defined Vandersypen. “These toggle the spin-spin change interplay between two completely different values, corresponding to 2 completely different qubit rotation axes. For 2-qubit gates, we activate the change coupling between spins belonging to completely different qubits, additionally utilizing gate voltage pulses.”
The researchers’ system is comprised of a 2 x 4 array of germanium quantum dots, forming a quantum dot ladder. By controlling the change interplay between every pair of spins alongside the rungs of this ladder, they initially mapped out the system’s qubit vitality spectrum.
The workforce subsequently realized common management of every qubit of their system by pulsing each the detuning and tunneling boundaries of the corresponding double quantum dot. By concurrently controlling these two boundaries of neighboring qubits, they finally attained a quantum gate that swaps data between qubits in a pair (i.e., two-qubit SWAP-style gate).
“When working this machine, all eight spins take part within the quantum coherent time evolution, which is essentially the most to this point in semiconductor quantum dot arrays,” added Vandersypen. “Our findings additionally spotlight the potential of the singlet-triplet qubit. Whereas the single-qubit operations are already fairly dependable, with a constancy above 99%, a vital subsequent step could be to indicate that the two-qubit gate will also be carried out with a constancy above 99%.”
This current work by Vandersypen and his colleagues introduces a promising strategy for attaining common management of germanium quantum dot-based methods with 4 singlet-triplet qubits. Sooner or later, this technique could possibly be improved additional to exactly manipulate even bigger nanoscale quantum methods.
The exact manipulation of those methods might enable physicists to reliably simulate advanced bodily phenomena, together with quantum magnetism. As well as, it might inform the event of extra superior quantum data methods.
Extra data:
Xin Zhang et al, Common management of 4 singlet–triplet qubits, Nature Nanotechnology (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41565-024-01817-9
© 2024 Science X Community
Quotation:
Researchers display common management of a quantum dot-based system with 4 singlet-triplet qubits (2024, November 13)
retrieved 13 November 2024
from Z1M
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.